
“Wherever technology reaches its real fulfillment, it transcends into architecture”
– Ludwig Meis van der Rohe
This quote explains the closely-knit relations between technology and architecture. The advent of modern visualization tools, modeling, and prototyping are redefining architecture and design. Such technological progress coupled with the dynamic nature of the industry constantly churns out new design styles.

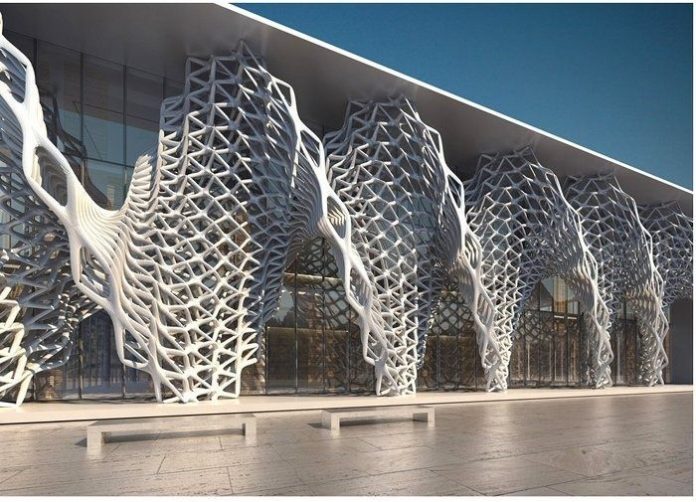
Parametric Building Design
Source: Pinterest
And, the latest design style that is reigning the AEC industry is parametricism. It is a computation-driven building design movement. The design style is spoken of as the successor to Modern and Postmodern architecture.
All Things Basic About Parametric Architecture
Labeled as a futuristic design style, parametric architecture challenges simple geometric forms by exploring a variety of complex form arrangements. The ultimate goal of parametricism is to create a building that is computer-calculated. It focuses on creating an abstract building design. Irregular forms and shapes, curvilinear geometry, and fluid lines are characteristics of parametric architecture.

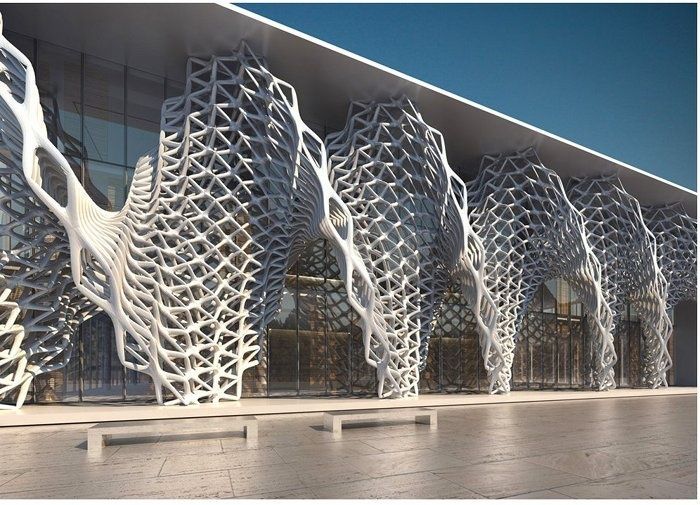
Parametric Architecture
Source: Autodesk
Often considered to be out worldly and futuristic, parametricism supports a modernist urban outlook through dynamic forms. It is considered that architects can create the impossible with parametricism. The central idea of a parametric design is to create inter-dependable and versatile structures. Such flexible design principles make parametricism largely applicable to even fashion and interior design.
The Journey of Parametricism in Architecture
The term “parametric architecture” has surfaced very recently in the AEC domain. However, its roots can be tracked down to as early as the 19th century with Antoni Gaudi’s most renowned work – La Sagrada Familia. The building’s representational models with hanging chains when flipped created the structure of a building.
Architect Luigi Moretti analyzed spatial relationships through parametric and mathematical equations in the 1960s. It is believed that these equations were used for planning the city of Rome. The term “parametric architecture” is considered to be first coined by Luigi himself. The first program or software that made use of these parametric equations was Sketchpad by Ivan Sutherland.
This further led to the discovery of three-dimensional modeling softwares by Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS) in 1989. The maiden terms of parametric modeling such as “wrap” and “fold” were invented in the initial version of the softwares developed by NURBS. These modeling systems form the most commonly used programs in contemporary parametric architecture. Imminent architects such as Zaha Hadid, Jean Nouvel, and Frank Gehry have contributed significantly to the use of parametricism in architecture.
Parametric Visualization and Facade Design
The process of Parametric Designing
Source: Pinterest
Computerized algorithms formulate the underlying principles of parametric architecture. Building dimensions are converted into parameters that form the basis of parametric modeling softwares such as Rhino and Grasshopper. The material and structural cohesiveness of the structure is considered by the software as it shapes the building parameters. The complex design so evolved is modular in nature and has a sculptural form but also proves to be highly functional.
Apart from Rhino and Grasshopper, the other softwares for parametric 3d modeling include SolidWorks and BIM. They are technologically well advanced and can help in determining the shape and size of building modules. The parametric design recognizes building bylaws and guidelines and provides relevant design solutions. They can also spot the building moment and shear analysis.
The out worldly and fancy conceptualization of parametricism is also reflected in its construction methods. 3D and 4D printing are prominent construction methods for parametric facades and buildings. 3D printing is the process of creating physical objects by consecutively laying down layers of construction materials. The objects are generally created in the form of modules which are then repetitively arranged to create a parametric facade or design.
Architectural Works of Parametric Design
Internationally, parametric architecture has taken over the regular linear geometry of buildings and painted them fancy. With the wide acceptability of parametricism in architecture, it can be manifested as the future of design.
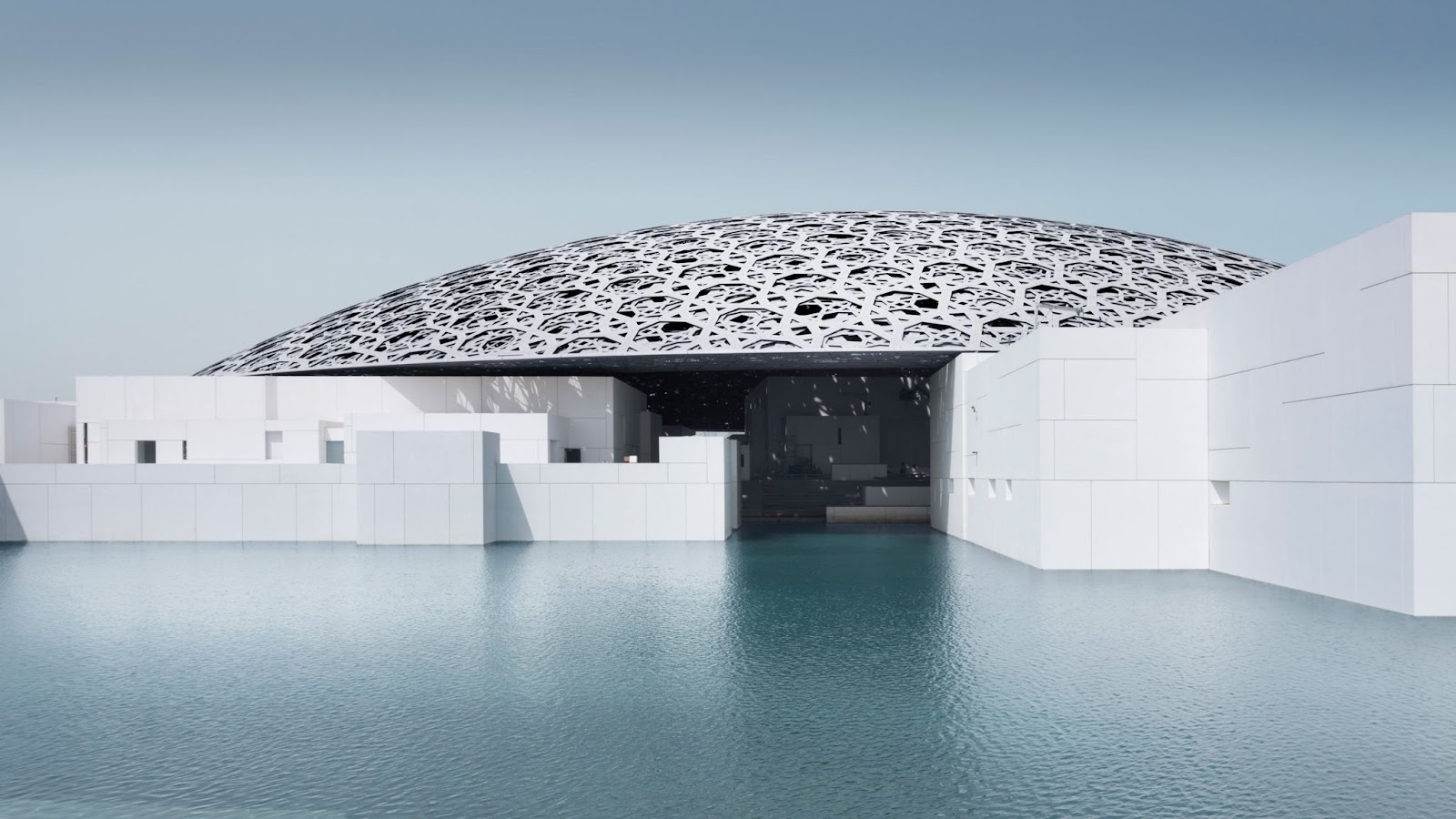

Louvre Abu Dhabi
Source: Conde Nast Traveler
The Louvre Abu Dhabi by the French architect Jean Nouvel is an excellent example of a parametric facade. Constructed in 2017, this 97,000 square metres of museum and exhibition space emphasizes the fascination generated by life experiences. The museum located in the middle of the sea is accessible by boat. The building accommodates bookstores, exhibit centres, and food outlets to experience the local cuisine. The museum design is both complex and serene.
The building design is considered to be inspired by Arab architecture, specifically the dome. However, the dome is interpreted through the modern lens and design with principles of parametricism. The double dome has a diameter of 180 metres designed in radiating geometry. It appears to be an organically woven material that provides shade through punctured surfaces. The dome also serves the purpose of protecting the landscape from the harsh Arab sunlight.
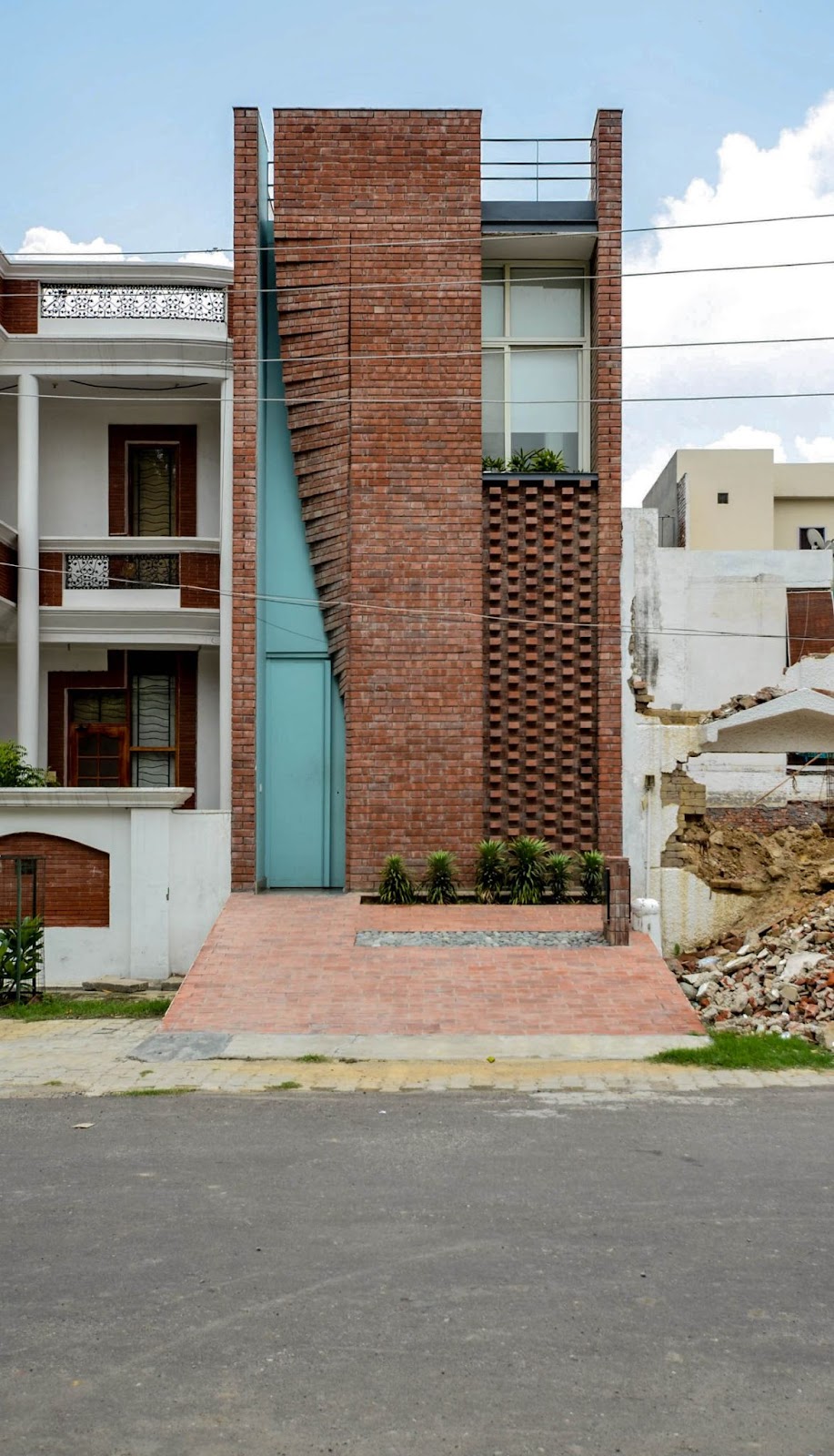

Brick Curtain Office
Source: ArchDaily
Closer to India, the Brick Curtain office in India by Firki Studio is a parametrically designed building. Located in Karnal, Haryana, the office is located on a residential street with no architectural character. With the intent of defining the design language of the area, the studio has planned the building as a landmark structure. The facade of the building is raw and earthy.
The west facade of the building is the only elevation that is accessible from the street. It is designed as a parametric facade with the idea of “entering from the street by moving aside a curtain” – which also gives the building its name. The intent was to make the building look inviting. The robustness of bricks and the softness of fabric-like form creates an interesting duality in design. The bricks are laid in succession by carefully twisting at 90 degrees through to the top of the facade. The other building elevations are composed of a combination of bricks and metal jali.

The Bad Cafe
Source: World Architecture Community
The works of Nuru Karim are inspirational in the field of parametric architecture. He works towards multi-disciplinary facets of architecture, art, and computational design. His design of The Bad Café in Bandra, Mumbai significantly draws a resemblance to parametric architecture. The building elevation is an envelope of black cylindrical skin made of recycled PVS electric conduits. These conduits are grafted into CNC’s aluminum composite box panels to create a seamless look. The building design inches closer to sustainability by depicting truth to material and blending the indoor and outdoor spaces.
Final Thoughts
Technology is elevating the scope of parametric architecture globally. The calculative precision that technology provides helps in creating error-free designs. Parametricism is a versatile facet of design that allows a building to seamlessly merge with nature. It adds to the beauty of the natural landscape by creating oneness with its forms and fluidity. Such flexibility brings us closer to achieving sustainability through design. The composition of breathable and comfortable facades by using the principles of parametric is helping create eco-friendly built spaces. While parametric architecture continues to flourish in today’s time and age, it is certain to be a significant element affecting the architecture of the future.
